IP address (internet protocol address) is a numerical label which is assigned to every device connected on the internet; desktop computer, laptop, printers, fax, security camera, smartphone, iPad, Tablet, smart watch, and even the routers.
The two main tasks achieved with the help of IP address includes
- the identification of the host interface, like what type of device the host is?
- provide the physical location of the host. This information helps reach to host with minimum hops route.
Functions of IP address
There are two main principal functions of and IP address.
- The first one is to identify the host or the container and the network interface.
- The second function is point out the location of the container in the network, finally establishes the path to reach to the host.
The role of an IP address can be simplified in three simple points;
- The name: the name indicates what we seek.
- The address: the address is to indicate where it is placed.
- The host: the last but not the least, how to reach to the host.
IP packet has two main parts:
- the host who is sending a request to a destination host,
- the destination host.
The versions
Commonly one may avail two categories of IP version on the internet. They are IP version 4 as well as IP version 6. Both are coming from the past decades. IP 4 started functioning in 1983. Later, after exhaustion of available IP addresses, IPv4 was modified to IPv6 in 1995.
Today it is possible to implement both the IP versions at the same time. The IP address is conveying the translation of the real message of the versions. They are supposed to stabilize the existence of the web link on the internet with proof.
Sub-networks
Although the IP versions are bifurcated into two branches, as mentioned earlier, still the recognition is investing more elaborates. An IP address can be recognized in two main parts.
- The network prefix is contained in the high-order bits. It is the central zone of the network.
- The one having lower bits which are called rest field, host identifier or interface identifier (IPv6).
Sub-mask is also in employ, and it may be acting as a sub-network. It has the idea of exploring the version in organized shape.
IPv4 address
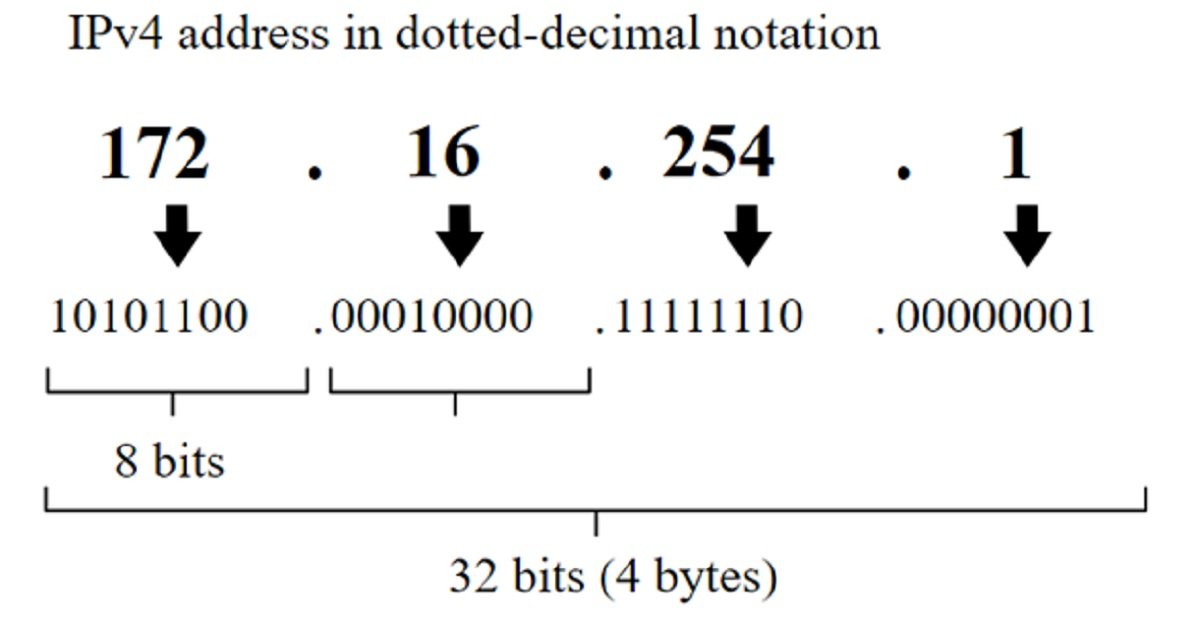 The first version of the IP address is called as IPv4 can contains a size of 32bits and contain 4,294,967,296 (2 32) addresses in total. From these addresses, some addresses are reserved as private address (~18 million addresses) and multicast addressing (~270 million addresses).
The first version of the IP address is called as IPv4 can contains a size of 32bits and contain 4,294,967,296 (2 32) addresses in total. From these addresses, some addresses are reserved as private address (~18 million addresses) and multicast addressing (~270 million addresses).
IPv4 are represented in dot-decimal notion, consisted of 4 decimal notions ranging from 0 to 255 and each notion is separated by a dot, e.g. 255.254.0.198. Each notion or group represents 8 bits or one octet of IPv4 IP address. IPv4 addresses can be presented in hexadecimal, octal, or binary representations.
Sub-netting
IPv4 IP addresses can be divided into two major groups. The first group is called global, or public, or external group – the IP addresses of this group are called WAN addresses – or for simplicity the ones that are used in the internet.
All the servers and sites on the internet use Public IP addresses. The other interesting thing about public IP addresses, they are unique to their host or server and cannot have a duplicate assignment.
The second group of IPv4 IP addresses is called private, or local, or internal addresses – this IP address pool is used in the local network (LAN). The private internal addresses are not routed over the internet. Hence no traffic cannot be sent to the pool of private IP addresses from the internet.
Private addresses include IP addresses from the following subnets:
- Range from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 — a 10.0.0.0 network with a 255.0.0.0 or an /8 (8-bit) mask.
- Range from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 — a 172.16.0.0 network with a 255.240.0.0 (or a 12-bit) mask.
- A 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 range, which is a 192.168.0.0 network masked by 255.255.0.0 or /16.
- A special range 100.64.0.0 to 100.127.255.255 with a 255.192.0.0 or /10 network mask; this subnet is recommended according to rfc6598 for use as an address pool for CGN (Carrier-Grade NAT).
IPv6 IP address
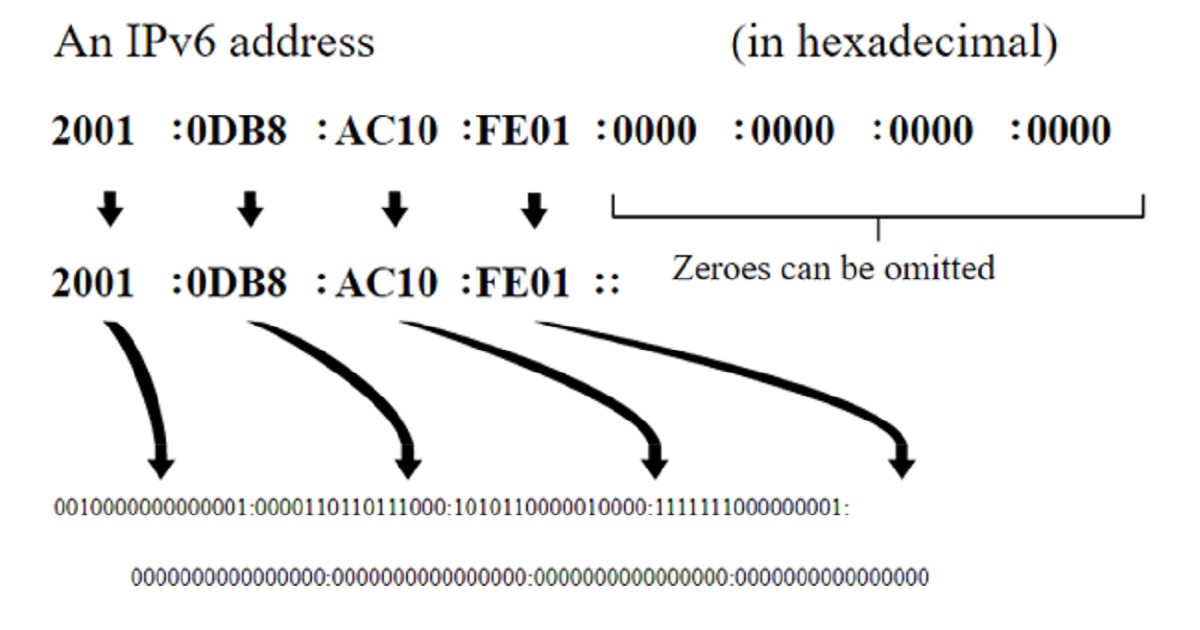 The IPv6 IP address is the upgraded version of the IPv4, from 32 bit to 128 bit IP address. In 6th version of IP address we can get up to 2128 (approximately 3.403×1038) addresses which is sufficient for the foreseeable future of mobile device included.
The IPv6 IP address is the upgraded version of the IPv4, from 32 bit to 128 bit IP address. In 6th version of IP address we can get up to 2128 (approximately 3.403×1038) addresses which is sufficient for the foreseeable future of mobile device included.
In IPv6, the sub-network routing prefix aggregation has made more efficient. Having IPv6, the need to increase in the routing tables has been decreased. With IPv6 IP address, the smallest possible individual allocation of 264 host in a subnet which is equal to the square of the entire IPv4 internet size.
Private addresses for IP address
Just like IPv4, there is a reserve pool of IPv6 IP addresses in IPv6 IP address. In IPv6, these are referred to as unique local addresses (ULAs).
How to find your public IP address?
When someone is using internet protocol through a computing device, it is not possible to identify it by the name of the device. To get a computing device identified on the world wide web (WWW) or a local area network (LAN) it is necessary to have an internet protocol number or an IP address for the device.
There are different IP addresses involved when a device is communicating over the internet or on a local area network. The first one is related to the communication over the internet and that is the IP address of your router. That address or number is assigned by your internet service provider (ISP). It is the router, in turn, handles all the traffic or communication from your computing device out to the internet. If you desire to see the IP address of your router, simply search for “What is my IP” on the Google and you will get to know the IP address of your router.
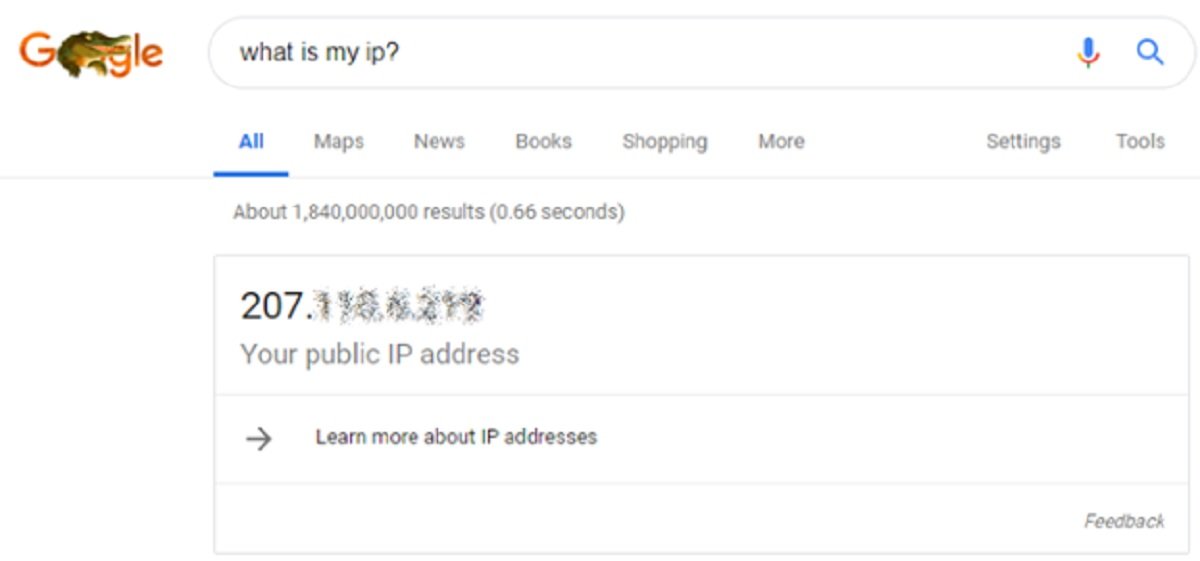
That decimal will be your public IP address which is connecting you to the world wide web (WWW).
How to find your internal IP address?
All the devices connected to the router of your internet service provider (ISP) create a local area network (LAN). These devices are then assigned an IP address by the router of your internet service provider (ISP) to create a local area network (LAN) for that particular router. To assign the the address to all the computing devices within the range of a router protocol is used which is called Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP).
It is important to note that the IP assigned by the router is “dynamic IP”, means it is temporary or stay assigned for the period a computing device is connected over the world wide web. Once the device is disconnected the assigned IP is available to be assigned to any other device.
In windows, to get to know your internal IP address, you need to go to command prompt by typing “cmd” in windows search. Once you are in the command prompt type “ipconfig” and enter.
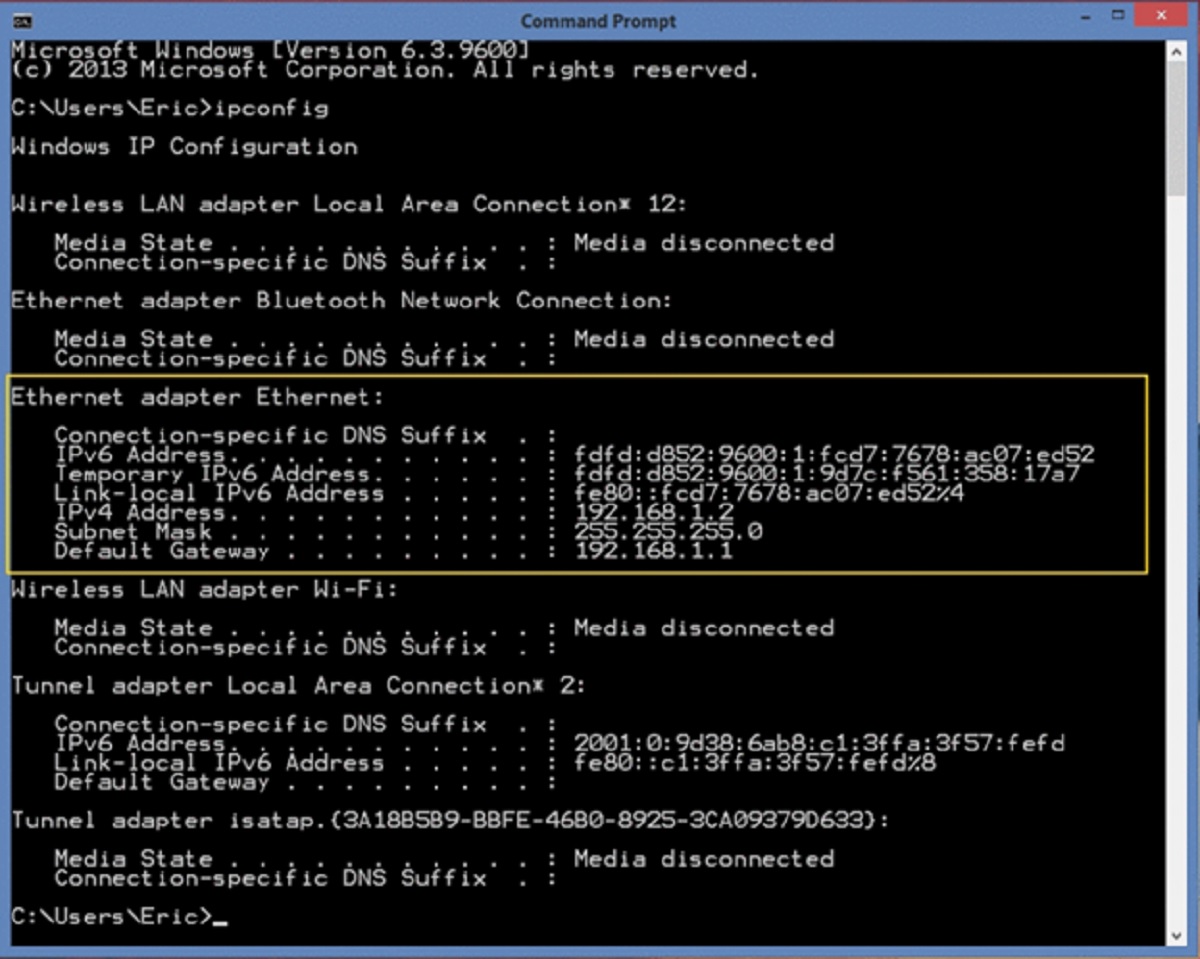
You can see the your internal IP address in the black screen.
Need of IPv6 over IPv4
32-bit IP addresses are shown in four decimals, also called as octet, separated by a dot and are called IPv4 address. The range of each these octet is from 0 to 255. The range of IPv4 address is from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255. This is the format of IP version 4 (or IPv4). The total number which the world can get is about 4+ billion, which is not so enough.
On contrary, the IP version 6 (or IPv6) is 128-bit decimal number and have four to 16 octets. In IPv6 the available IP addresses are 34 with 37 zeros or 2 to the 128th power or technically speaking 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,455. It means every square foot of the earth can have an IP address and that’s a lot. That’s good to know, isn’t it?
Yep, we know that is a lot information! But after reading this article, we hope everything is clarified. If you have any comment, please feel free to use the comments box below.



What Does Wi-Fi Actually Mean? The Surprising Truth and How It Works
IoT Machine Learning 2026: From Connected Sensors to Autonomous Agents